Advancements in Targeted Drug Therapies for Chronic Pain Management
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in targeted drug therapies for chronic pain management. These breakthroughs have offered new hope for individuals suffering from persistent and debilitating pain conditions. One of the most promising developments in this field is the utilization of monoclonal antibodies to target specific pain receptors in the body. By blocking the activity of these receptors, these drugs can effectively reduce the transmission of pain signals, providing relief for patients with conditions such as neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia.
Furthermore, the advent of gene therapy has opened up new possibilities for personalized pain management. Researchers are exploring the potential of using gene editing techniques to modify the expression of pain-related genes, offering a tailored approach to addressing chronic pain based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. This level of precision in targeting the underlying mechanisms of pain holds great promise for improving the effectiveness of pain relief treatments while minimizing side effects.
Another area of significant progress is the development of novel drug delivery systems that allow for the targeted and sustained release of pain medications. Utilizing nanotechnology, researchers have been able to design drug carriers that can selectively deliver pain-relieving agents to specific sites of injury or inflammation, providing localized and prolonged relief. These advancements not only enhance the efficacy of pain management but also reduce the overall dosage of medications required, thereby lowering the risk of systemic side effects.
In conclusion, the latest breakthroughs in targeted drug therapies for chronic pain management represent a paradigm shift in the approach to treating persistent pain conditions. With ongoing research and technological innovations, the future holds great promise for the development of even more effective and individualized pain relief solutions.
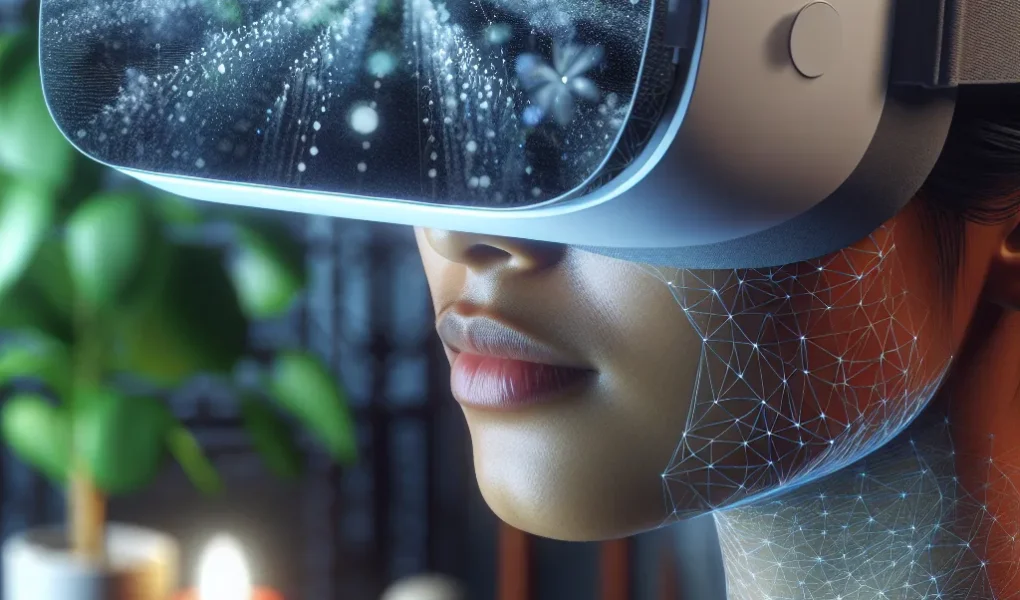
The Integration of Virtual Reality Technology in Pain Distraction Techniques
In recent years, there have been exciting breakthroughs in pain relief research, particularly in the integration of virtual reality (VR) technology in pain distraction techniques. VR has emerged as a promising tool in managing both acute and chronic pain by redirecting patients’ attention away from their discomfort. By immersing individuals in captivating virtual environments, VR has demonstrated remarkable potential in altering the perception of pain.
Studies have shown that VR distraction can significantly reduce the intensity of pain experienced during medical procedures, such as wound care, dental treatments, and physical therapy sessions. Furthermore, the use of VR in chronic pain management has exhibited encouraging results, offering patients a non-pharmacological intervention that can enhance their overall well-being.
One of the key advantages of VR technology in pain relief is its ability to create multisensory experiences, engaging not only the visual sense but also auditory and tactile stimuli. This multisensory immersion can effectively modulate the brain’s processing of pain signals, providing a more comprehensive distraction from the discomfort.
Moreover, VR has the potential to personalize pain distraction experiences, allowing individuals to choose environments that resonate with their preferences, from serene nature scenes to dynamic adventures, empowering them with a sense of agency over their pain management journey.
As the field of pain relief continues to evolve, the integration of VR technology in distraction techniques represents a promising avenue for enhancing patient care and improving the overall experience of pain management.
Exploring the Role of Genetics in Individualized Pain Management Strategies
Recent breakthroughs in pain relief research have led to a better understanding of the role genetics play in individualized pain management strategies. Scientists are now delving into the intricate world of genetic makeup to uncover how it influences one’s response to pain and, more importantly, how it can revolutionize the way we approach pain relief treatments.
The study of genetics in pain management has unveiled the significant variability in how individuals perceive and respond to pain. Variations in genes can affect the expression of pain receptors, neurotransmitters, and other molecular targets involved in the pain pathway. By identifying these genetic markers, healthcare professionals can potentially tailor pain management strategies to suit each individual’s unique genetic profile, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized treatments.
Advancements in genetic testing have paved the way for the development of innovative tools that can analyze an individual’s genetic predisposition to certain types of pain and predict their response to specific medications. This personalized approach to pain management holds great promise in optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
In addition to refining traditional pain relief methods, such as medication and physical therapy, the insights gained from genetic research are driving the exploration of novel therapeutic targets. By honing in on the genetic factors underlying pain, researchers are identifying potential new drug targets and pathways that may lead to the development of groundbreaking pain relief interventions tailored to an individual’s genetic profile.
As the field of genetics continues to unravel the complexities of pain perception and management, the future holds tremendous potential for customized, genetically informed pain relief strategies that could significantly improve the quality of life for millions of individuals suffering from chronic or acute pain.
Innovative Non-Pharmacological Approaches to Pain Relief
Recent breakthroughs in pain relief research have led to innovative non-pharmacological approaches that are changing the way we manage pain. One of the most promising developments is the use of virtual reality (VR) technology to alleviate chronic and acute pain. Studies have shown that immersive VR experiences can distract patients from their pain, reducing the need for traditional pain medications.
Another cutting-edge non-pharmacological approach involves transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), which uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain. This approach has been found to be particularly effective for managing musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain, offering a non-invasive alternative to medication.
Furthermore, mindfulness meditation and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have gained recognition for their efficacy in pain management. These practices help patients develop coping strategies and change their relationship with pain, leading to long-term reductions in pain perception and improvement in overall quality of life.
These non-pharmacological approaches to pain relief represent a new frontier in the field of pain management, offering patients effective alternatives to traditional medications and paving the way for a more holistic approach to treating pain.
The Impact of Neurostimulation and Neuromodulation on Pain Management
Sure, here is a fragment of the article:
Neurostimulation and neuromodulation have emerged as groundbreaking approaches in the field of pain management, offering new hope for individuals suffering from chronic and debilitating pain conditions. These innovative techniques harness the power of electrical impulses to target and modulate specific regions of the nervous system, providing significant relief for patients who have not found success with traditional treatments.
One of the most notable breakthroughs in neurostimulation is the development of spinal cord stimulation (SCS), which involves the implantation of a small device that delivers electrical pulses to the spinal cord. This targeted stimulation disrupts the transmission of pain signals to the brain, effectively reducing the perception of pain. Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of SCS in treating various types of chronic pain, including neuropathic pain, failed back surgery syndrome, and complex regional pain syndrome.
Similarly, neuromodulation techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) have shown promise in providing relief for individuals with conditions such as migraines, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. By modulating the activity of specific brain regions involved in pain processing, these non-invasive approaches offer a novel avenue for managing pain without the use of medications.
The impact of neurostimulation and neuromodulation on pain management extends beyond symptom relief, as these modalities also carry the potential to improve overall quality of life for patients. By reducing the reliance on opioid medications and offering long-term pain relief, these interventions have the capacity to enhance physical function, mental well-being, and social engagement for individuals grappling with chronic pain.
In conclusion, the integration of neurostimulation and neuromodulation techniques marks a significant advancement in the management of pain, offering hope and healing for those who have previously been burdened by unrelenting pain. As research in this field continues to evolve, the future holds promise for further refinements in these approaches, ultimately improving the lives of countless individuals struggling with chronic pain.
The Promise of Cannabinoids and Cannabis-Derived Medicines in Pain Relief Research
Recent years have seen a surge of interest and research into the potential of cannabinoids and cannabis-derived medicines in the field of pain relief. The promise of these substances lies in their ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors involved in regulating various physiological processes, including pain sensation. Cannabinoids, the active compounds found in cannabis, have shown promise in mitigating both acute and chronic pain.
One of the most well-known cannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), has been found to have analgesic properties, offering relief from pain by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system. On the other hand, cannabidiol (CBD), another prominent cannabinoid, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, potentially contributing to its pain-relieving capabilities.
Moreover, the endocannabinoid system’s intricate involvement in pain modulation has prompted researchers to explore the therapeutic potential of cannabis-derived medicines in conditions such as neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and even cancer-related pain. By leveraging the synergistic effects of various cannabinoids and terpenes, scientists are striving to develop targeted and effective treatments that minimize the side effects commonly associated with conventional pain medications.
Despite the promising findings, it’s important to note that further clinical trials and rigorous studies are essential to substantiate the efficacy and safety of cannabinoids and cannabis-derived medicines in pain relief. Additionally, addressing regulatory challenges and standardizing formulations will be crucial in harnessing the full potential of these substances for managing pain.
In conclusion, the burgeoning research into cannabinoids and cannabis-derived medicines offers a glimpse of hope for individuals suffering from debilitating pain. As scientists delve deeper into understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of these compounds, it is conceivable that the future of pain relief could be revolutionized by integrating the power of cannabinoids into mainstream medical practice.